UNSW team develops hydrogen fuel retrofit system for diesel engines
ENGINEERS from the University of New South Wales (UNSW) Sydney have successfully converted a diesel engine to run as a hydrogen-diesel hybrid engine – reducing CO2 emissions by more than 85 percent in the process.
The team, led by Professor Shawn Kook from the School of Mechanical and Manufacturing Engineering, spent about 18 months developing the Hydrogen-Diesel Direct Injection Dual-Fuel System that means existing diesel engines can run using 90 percent hydrogen as fuel.
The researchers claim any diesel engine used in trucks and power equipment in the transportation, agriculture and mining industries could ultimately be retrofitted to the new hybrid system in just a couple of months.
Green hydrogen, which is produced using clean renewable energy sources such as wind and solar, is much more environmentally friendly than diesel.
In a paper published in the International Journal of Hydrogen Energy, Prof. Kook’s team showed that using their patented hydrogen injection system reduced CO2 emissions to just 90 g/kWh – 85.9 percent below the amount produced by the diesel powered engine. 
“This new technology significantly reduces CO2 emissions from existing diesel engines, so it could play a big part in making our carbon footprint much smaller, especially in Australia with all our mining, agriculture and other heavy industries where diesel engines are widely used,” Prof. Kook said.
“We have shown that we can take those existing diesel engines and convert them into cleaner engines that burn hydrogen fuel.
“Being able to retrofit diesel engines that are already out there is much quicker than waiting for the development of completely new fuel cell systems that might not be commercially available at a larger scale for at least a decade.
“With the problem of carbon emissions and climate change, we need some more immediate solutions to deal with the issue of these many diesel engines currently in use.”
High-pressure hydrogen direct injection
The UNSW team’s solution to the problem maintains the original diesel injection into the engine, but adds a hydrogen fuel injection directly into the cylinder.
The collaborative research, performed with Dr Shaun Chan and Professor Evatt Hawkes, found that specifically timed hydrogen direct injection controlled the mixture condition inside the cylinder of the engine, which resolved the problem of harmful nitrogen oxide emissions that have been a major hurdle for commercialisation of hydrogen engines. 
“If you just put hydrogen into the engine and let it all mix together you will get a lot of nitrogen oxide (NOx) emissions, which is a significant cause of air pollution and acid rain,” Prof. Kook said.
“But we have shown in our system if you make it stratified – that is in some areas there is more hydrogen and in others there is less hydrogen – then we can reduce the NOx emissions below that of a purely diesel engine.”
Importantly, the new Hydrogen-Diesel Direct Injection Dual-Fuel System does not require extremely high purity hydrogen which must be used in alternative hydrogen fuel cell systems and is more expensive to produce.
Compared with existing diesel engines, an efficiency improvement of more than 26 percent has been shown in the diesel-hydrogen hybrid.
That improved efficiency is achieved by independent control of hydrogen direct injection timing, as well as diesel injection timing, enabling full control of combustion modes – premixed or mixing-controlled hydrogen combustion.
Fast-track to commercialisation
The research team hopes to be able to commercialise the new system in the next 12 to 24 months and are keen to consult with prospective investors.
They claimed the most immediate potential use for the new technology was in industrial locations where permanent hydrogen fuel supply lines are already in place.
That includes mining sites, where studies have shown that about 30 percent of greenhouse-gas emissions are caused by the use of diesel engines in such items as mining vehicles and power generators.
The Australian market for diesel-only power generators is currently estimated to be worth around $765 million.
“At mining sites, where hydrogen is piped in, we can convert the existing diesel engines that are used to generate power,” Prof. Kook said. 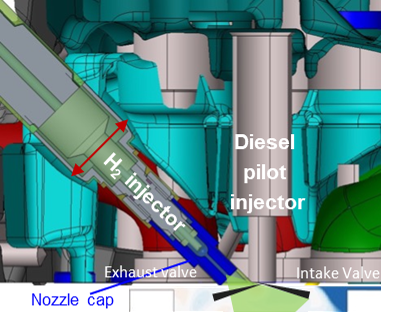
“In terms of applications where the hydrogen fuel would need to be stored and moved around, for example in a truck engine that currently runs purely on diesel, then we would also need to implement a hydrogen storage system to be integrated into our injection system.
“I do think the general technology with regards to mobile hydrogen storage needs to be developed further because at the moment that is quite a challenge.”
ends

 How to resolve AdBlock issue?
How to resolve AdBlock issue?